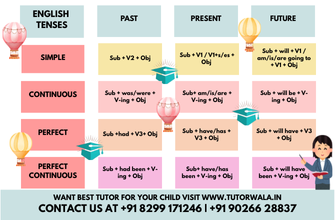
There are only three verb tenses in English grammar: Past, Present, and Future. Each of these has four aspects: Simple, Continuous (or Progressive), Perfect, and Perfect Continuous. This makes a total of 12 ordinary tenses.
The following is each tense's rule and example:
1. Present Tenses
1.1. Present Simple (or Simple Present)
- Rule: Base form of the verb. Append '-s' or '-es' for third-person singular subjects (he, she, it).
- Formula: Subject + V1 (base form) / V1 + s/es (for he/she/it)
- Uses:
- To describe habits or repeated actions.
- Example: She drinks tea every morning.
- To declare general truths or facts.
- Example: Water freezes at zero degrees Celsius.
- For fixed schedules or arrangements (most commonly for future events).
- Example: The train leaves at 7:00 PM.
- To provide instructions or directions.
- Example: You turn right at the corner.
- Examples:
- I walk to school.
- He plays football.
- They study English.
1.2. Present Continuous (or Present Progressive)
- Rule:Present tense of "to be" (am, is, are) + present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
- Formula:Subject + am/is/are + V-ing
- Uses:
- To tell what is happening at the time of speaking.
- Example: I am writing an email right now.
- In order to talk about things that are occurring around the current moment, although not necessarily at the actual time.
- Example: She is preparing for her exams this week.
- For arranged future situations (scheduled appointments).
- Example: We are having dinner with them tomorrow night.
- In order to talk about temporary circumstances.
- Example: He is staying with his aunt this month.
- With "always," "constantly," "forever" to talk about repetitive, frequently annoying behaviors.
- Example: You are always grumbling!
- Examples:
- She is singing.
- They are playing in the park.
- I am reading a book.
1.3. Present Perfect
- Rule:"Have" or "has" + past participle (V3) of the main verb.
- Formula:Subject + have/has + V3
- Uses:
- To describe actions which occurred at some time in the past, but have a bearing on the present.
- Example: I have visited Paris twice. (The experience is relevant now)
- In order to explain actions that began in the past and extend to the present time.
- Example: She has lived in London for five years.
- For recent actions, usually with "just."
- Example: He has just finished his homework.
- To discuss experiences up to the current point.
- Example: Have you ever eaten sushi?
- Examples:
- They have seen that movie.
- She has begun a new job.
- I have lost my keys.
1.4. Present Perfect Continuous (or Present Perfect Progressive)
- Rule:"Have been" or "has been" + present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
- Formula:Subject + have/has + been + V-ing
- Uses:
- To describe actions that began in the past and continued up to the present moment. The focus is on the length of time.
- Example: She has been studying for three hours.
- To state actions which have recently concluded, but their results are apparent or still applicable in the current time.
- Example: I'm exhausted since I have been running.
- Examples:
- It rained throughout the morning.
- They waited for you for one hour.
- He has been working on this project since last month.
2. Past Tenses
2.1. Past Simple (or Simple Past)
- Rule:For regular verbs, append '-ed' to the base form. For irregular verbs, append their own past tense form.
- Formula:Subject + V2 (past form)
- Uses:
- To describe completed actions or events that occurred at a particular moment in the past.
- Example: I went to the store yesterday.
- To describe a chain of completed actions in the past.
- Example: She woke up, ate breakfast, and left for work.
- To refer to habits or routines in the past.
- Example: As a child, I played outside daily.
- Examples:
- He watched a movie last night.
- They completed their work.
- She resided in Japan.
2.2. Past Continuous (or Past Progressive)
- Rule:"Was" or "were" + present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
- Formula:Subject + was/were + V-ing
- Uses:
- To state an action which was ongoing at some point in the past.
- Example: I was having dinner at 8 PM last night.
- To state an action which was still ongoing in the past but was interrupted by some action.
- Example: I was reading when the phone rang.
- To state two or more actions occurring simultaneously in the past.
- Example: My brother was watching television while I was cooking.
- To define the background environment in a narrative.
- Example: The sun was shining and birds were singing.
- Examples:
- She was studying when I phoned.
- They were playing basketball.
- It snowed all day yesterday.
2.3. Past Perfect
- Rule:"Had* + past participle (V3) of the main verb.
- Formula:Subject + had + V3
- Uses:
- To explain an action that was finished before another action in the past. It makes the order of events clear.
- Example: By the time I arrived, she had already left. (First she left, then I arrived).
- To express a cause-and-effect relationship in the past.
- Example: He was tired because he had worked all night.
- In reported speech.
- Example: She said she had seen him before.
- Examples:
- I had eaten dinner before they arrived.
- They had finished the project by Friday.
- She had never seen such a beautiful sunset before that day.
2.4. Past Perfect Continuous (or Past Perfect Progressive)
- Rule:"Had been" + present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
- Formula:Subject + had + been + V-ing
- Uses:
- To talk about an action that was being done for some amount of time in the past, up to some other definite point in the past.
- Example: She had been waiting for two hours before the bus finally arrived.
- To describe the cause of a past event.
- E.g.: His eyes were red because he had been crying.
- Examples:
- They had been living there for ten years when they made the decision to move.
- I had been learning English for five years before I moved to England.
- He had been running, so he was short of breath.
3. Future Tenses
3.1. Future Simple (or Simple Future)
- Rule:"Will" + base form of the main verb. (Also, "be going to" + base form is standard for future plans/predictions).
- Formula:Subject + will + V1
- Alternative:Subject + am/is/are + going to + V1
- Anticipated uses:
- For predictions about the future.
- Example: It will rain tomorrow.
- For spontaneous decisions or offers.
- Example: I will help you with that.
- For promises or intentions.
- Example: I will call you later.
- For future facts.
- Example: The sun will be rising at 6 AM.
- "Be going to" is usually employed in making arrangements or intentions, or in making predictions on the basis of current evidence.
- Example: I am going to see my grandmother next week. (Arrangement)
- Example: Look at clouds; it's going to rain. (Prediction based on evidence)
- Examples:
- She will be traveling next year.
- They are going to construct a new house.
- I will be seeing you soon.
3.2. Future Continuous (or Future Progressive)
- Rule:"Will be" + present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
- Formula:Subject + will be + V-ing
- Uses:
- To describe an action that will be going on at a particular point in the future.
- Example: At 10 AM tomorrow, I will be working.
- To describe an action that will be in progress when another future action is taking place.
- Example: When you arrive, I will be cooking dinner.
- To inquire politely about the plans of someone.
- Example: Will you attend the party this evening?
- Examples:
- He will be studying throughout the evening.
- They will have dinner upon our arrival.
- I will be waiting for you at the station.
3.3. Future Perfect
- Rule:"Will have" + the past participle (V3) of the main verb.
- Formula:Subject + will have + V3
- Uses:
- To indicate an action to be finished prior to a point in the future.
- Example: I will have graduated from university by next year.
- To convey an assumption regarding something already done.
- Example: He will have come by now.
- Examples:
- She will have completed her report by 5 PM.
- They will have constructed the bridge by 2030.
- I will have read this book by the end of the week.
3.4. Future Perfect Continuous (or Future Perfect Progressive)
- Rule:"Will have been" + present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
- Formula:Subject + will have been + V-ing
- Uses:
- To express an action that will have been in progress for a specific period up to some time in the future. The stress is placed on the period leading up to that future time.
- Example: In November, I will have worked for five years at this company.
- To indicate the cause of an event in the future.
- Example: After he completes his marathon, he will have been running for four hours.
- Examples:
- By the time she goes to bed at midnight, she will have slept for six hours.
- They will have been on the road for 24 hours when they arrive at their destination.
- I will have been waiting for him for an hour when he finally arrives.
Understanding these tenses and their applications is crucial for effective communication in English.
.